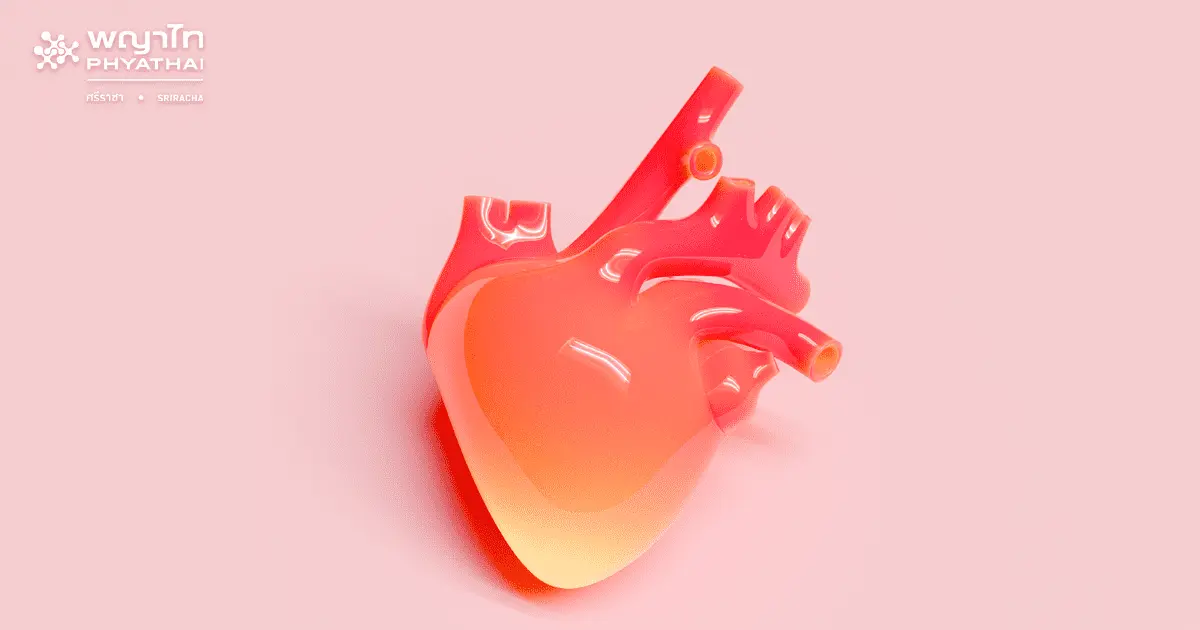
Many people already know that coronary artery disease is one of the leading causes of sudden death among Thais, and the trend continues to rise. When it comes to coronary artery blockage, the first cause that comes to mind is probably the buildup of fatty plaque in the arteries. However, in reality, arterial blockage is not solely caused by fatty plaque but also by the accumulation of calcium, also known as "limestone."
For further information or Booking..
What causes limestone in the arteries?
Limestone refers to the accumulation of calcium in our bodies, which forms hardened deposits. It can occur due to various reasons, including natural wear and tear of calcium or inflammation at specific sites. The body’s mechanism creates calcium to protect injured areas from further damage. Limestone can also attach itself to fatty plaque in the arteries, leading to arterial stiffness and blockages. Studies have found that even a small amount of calcium or limestone deposits in the walls of the coronary arteries increases the risk of coronary artery disease and can potentially lead to sudden cardiac arrest in the future.
Knowing… by detecting limestone in the coronary arteries
We cannot determine when these limestone deposits begin to form in our arteries until clear symptoms of coronary artery blockage occur or, unfortunately, after experiencing a heart attack. Detecting limestone deposits in the walls of the coronary arteries is, therefore, the best way to stay informed and prepared for potential risks.
Coronary Calcium Score, a method for detecting calcium or limestone deposits in the coronary arteries, involves calculating the amount of calcium attached to the walls of the arteries using high-speed computed tomography (CT scan) with high resolution. This method accurately determines the quantity of limestone accumulated in the coronary arteries and provides insights into the likelihood of experiencing sudden coronary artery blockage. If no limestone deposits are detected, the calcium score will be 0, indicating a low risk of developing coronary artery blockage or sudden heart muscle ischemia in the future. However, if the calcium score is high, especially above 400, there is a higher risk of coronary artery disease within the next 2-5 years, even without any apparent symptoms.
Benefits you should know Because silent diseases are often dangerous, detecting calcium deposits in the coronary arteries can help physicians assess the situation and plan appropriate treatment to reduce the risk of future heart artery-related deaths.
- Takes about 10 minutes for the examination.
- No need for injection of dye.
- No need to stay in the hospital.
- No special preparation required before the examination.
Who should get tested?
• Individuals with a family history of heart artery disease.
• Individuals aged 45 and above, both males and females, especially menopausal women.
• Individuals with high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes.
• Smokers.
• Individuals who are overweight.
Can you prevent calcium deposits in the arteries? It may be difficult for us to control the occurrence of calcium deposits in our bodies, but what we can do and should do regularly is take care of our bodies, eat a healthy diet, exercise regularly, get enough rest, relax and relieve stress, and have a health check-up at least once a year.
For further information or Booking..