For further information or Booking..
Making Test Tube Babies: The IVF and ICSI Procedures
The process of creating test tube babies using in vitro fertilization (IVF) and intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) involves several important steps that make it easier for individuals experiencing fertility difficulties to conceive. Here are the seven key steps involved:
1. Ovarian Stimulation:
On the second or third day of the menstrual cycle, blood tests are conducted to measure the levels of sex hormones in the body. This helps assess the functioning of the ovaries. An ultrasound is also performed to count the number of developing eggs produced during that menstrual cycle.
Ovarian stimulation involves the administration of medication to stimulate egg production. Typically, injections are used for ovarian stimulation, and there are various protocols for this process. At the Phyathai Sriracha Hospital, they use a single protocol that is convenient and effective. The stimulation starts on the second or third day of the menstrual cycle, following the evaluation of hormone levels and ultrasound results. The dosage of the stimulation medication is adjusted individually based on hormone levels, ultrasound findings, and the age of the female partner. Generally, there are approximately 2-3 types of medications used for ovarian stimulation.
The first type is recombinant FSH), which stimulates the growth of multiple eggs and is administered for about five days. Afterward, the second type of medication, GnRH antagonist, is used to prevent premature egg release. This medication is crucial when multiple eggs are present. If the eggs are not protected from premature release, they may be lost before they can be retrieved.
The suitable duration for continuous ovarian stimulation is 10-12 days. During this period, hormone levels are monitored, and ultrasound examinations are performed approximately three times to track the growth of the eggs. The date for egg retrieval is determined based on the size of the eggs. Generally, eggs with a suitable size for retrieval should be around 18 mm or larger. The final medication administered is hCG, which triggers egg maturation. The eggs are then released within the next 36 hours.

2. Egg Retrieval:
Egg retrieval is performed through the vaginal canal using a small needle attached to an ultrasound probe. The ultrasound probe helps locate the eggs during the aspiration procedure. The retrieval is conducted under anesthesia after the patient is sedated. The eggs are suctioned out using ultrasound guidance, and the procedure typically takes less than half an hour. The collected fluid containing the eggs is examined under a microscope to identify and separate the eggs. The retrieved eggs are then placed in a culture medium for preparation before the fertilization process.

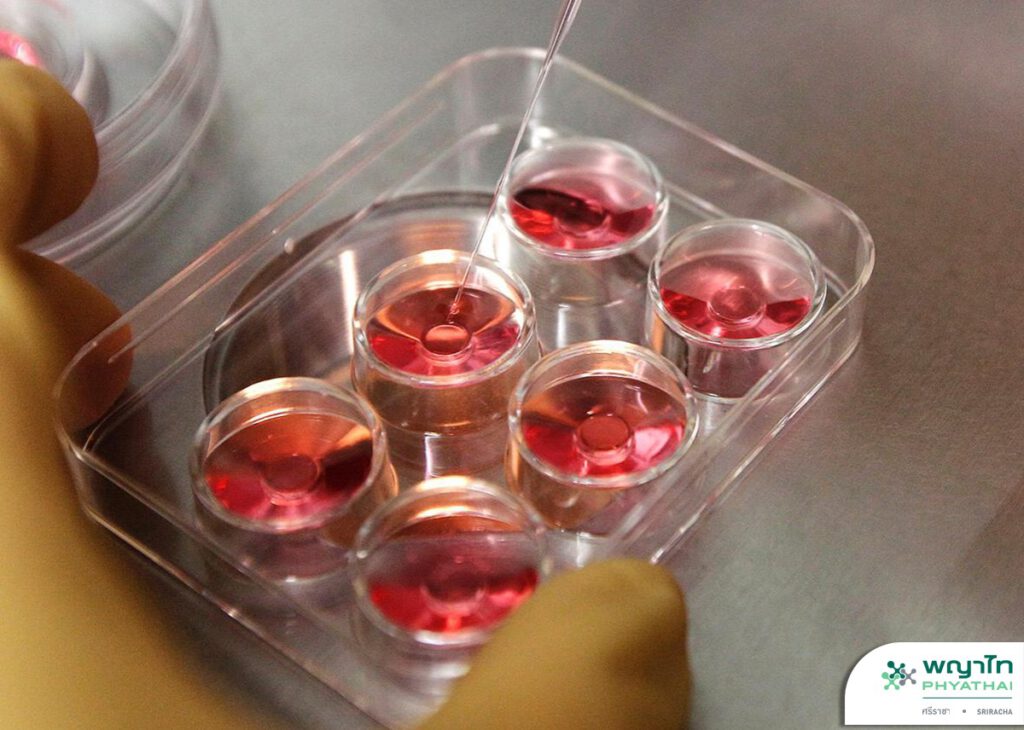
3. Collection and Separation of Sperm
The separation of sperm from seminal fluid is done to prepare the sperm for fertilization. The male partner should abstain from sexual intercourse for approximately 3 to 7 days. The semen sample is collected using a sterile container specifically designed for assisted reproductive techniques. The collected semen sample needs to be delivered to the laboratory within half an hour after ejaculation to ensure the viability of the sperm. Otherwise, the sperm’s fertilization capability may decrease. The separated sperm will be supplemented with nutrients to enhance motility and prepare them for further fertilization.
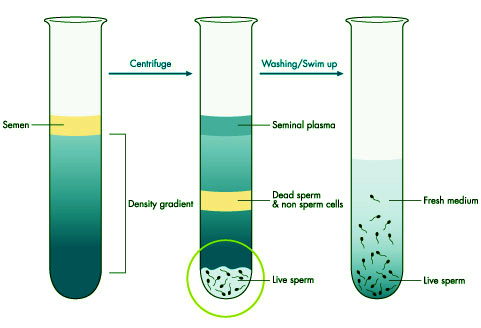
The process involves washing the sperm sample through a layer of separation medium and centrifugation to remove impurities. After separation, the viable sperm will be mixed with the eggs for fertilization.
4. Fertilization of Eggs with Sperm
In the case of conventional in vitro fertilization (IVF) for the production of embryos, the sperm is allowed to swim and fertilize the eggs naturally. An adequate number of viable sperm is added to the eggs and left for a suitable duration. Afterward, the fertilization is examined to determine if embryonic development has occurred. This method may not be suitable for male partners with low sperm count or poor sperm quality below the standard threshold, as there is a high risk of unsuccessful fertilization. In such cases, intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) is recommended.
5. Embryo Culturing
The embryos are cultured in an incubator with controlled temperature conditions to promote cell division. From one cell, they divide into two cells, four cells, and then eight cells. Afterward, the embryos undergo a selection process to either transfer them back into the uterus or continue culturing to develop into blastocyst-stage embryos.
6. Embryo Transfer into the Uterus
The process of transferring embryos back into the uterus is similar to a regular internal examination. It does not require anesthesia or induce significant pain. However, in certain cases where the female partner cannot undergo vaginal instrument insertion or experiences extreme anxiety, the use of anesthesia can facilitate a smoother embryo transfer process.
Embryonic Transfer Techniques in Ants
The process of transferring ant larvae begins with the use of extremely small larval transfer threads. The larvae are sucked and passed through the queen’s mouth, where they are placed on the brood chamber epithelium. Generally, using ultrasound to locate the most suitable spot for larval placement increases the chances of successful impregnation compared to transferring larvae without ultrasound. This is due to the anatomical differences in the female’s reproductive system.


7. Cryopreservation of Remaining Larvae
Cryopreserving the remaining larvae after larval transfer is a method that significantly increases the chances of successful impregnation compared to traditional glass tube insemination methods. With the developed cryopreservation techniques, we can now store and preserve larvae for several years and later transfer them without the need to stimulate new eggs.
The epithelium developed during the larval transfer cryopreservation process grows naturally, unlike the epithelium developed during egg stimulation, which has a tendency to overgrow beyond the egg’s growth potential. Therefore, transferring fresh larvae may not be suitable for successful larval implantation due to excessive development of the epithelium. Consequently, cryopreserving and transferring larvae may yield better results, especially when multiple eggs are stimulated

There are various methods of cryopreservation currently available. Phyathai Siriracha Hospital has developed a technique called vitrification and prepared specific cryopreservation solutions without the need for imports from other countries. They have nearly a decade of experience in cryopreserving larvae using this method, which has shown a survival rate of over 95% after larval dissolution, with larvae having the potential to develop into post-embryonic stages similar to those not subjected to cryopreservation.
Therefore, it can be confidently concluded that larval transfer can be performed both with fresh larvae immediately after collecting eggs and with cryopreserved larvae. Cryopreservation offers higher chances of successful larval implantation due to the use of high-quality preservation techniques.














