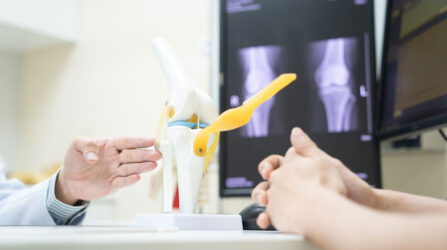
Osteoarthritis is a slowly progressive disease that often presents with no clear symptoms in its early stages, leading many individuals to remain unaware of their condition.
For further information or Booking..
Osteoarthritis is a common inflammatory joint condition characterized by the gradual deterioration of cartilage—the soft, cushioning tissue at the ends of bones within a joint. This cartilage functions as a shock absorber and facilitates smooth, pain-free joint movement. Over time, it can wear down, leading to joint pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility.
Individuals at Risk
- Age 50 and Above: Both men and women who perform physically demanding tasks or repetitive movements are at increased risk.
- Age 70 and Above: Osteoarthritis affects 80–90% of individuals in this age group.
- Overweight Individuals: Excess body weight accelerates wear and tear, particularly in weight-bearing joints like the knees and hips.
- Occupational Risk: Jobs that require repetitive joint use or poor posture (e.g., prolonged kneeling, sitting cross-legged) can increase the risk.
- History of Joint Conditions: People with rheumatoid arthritis, past joint infections, or joint injuries are more susceptible to osteoarthritis.
Symptoms of Osteoarthritis
- Audible Sounds: Clicking or popping noises may occur during joint movement. New bone growth may form as the body attempts to stabilize the joint.
- Pain and Discomfort: Bone-on-bone friction can cause pain during movement. In some cases, persistent pain limits mobility and leads to muscle weakness.
- Stiffness: Especially noticeable in the morning or after periods of inactivity.
- Joint Deformities: Such as bowlegs or outward-turning knees, often accompanied by a limited range of motion.
Diagnostic Methods
- Physical Examination: Evaluation by a specialist in bone and joint disorders.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays or MRI scans to assess the joint structure.
- Bone Mass Density Measurement: Bone densitometry (BMD) can be used to evaluate bone health, especially in cases with overlapping conditions like osteoporosis.
Treatment Guidelines for Osteoarthritis
- Physical Therapy: Custom-tailored rehabilitation programs aimed at muscle relaxation, strengthening, and pain reduction.
- Medications: Anti-inflammatory drugs and pain relievers help patients maintain a near-normal quality of life.
- Joint Injections: Injection of lubricating substances or synthetic joint fluid to reduce friction and relieve pain.
- Arthroscopic Debridement: A minimally invasive procedure using a camera to diagnose and clean the joint, smooth surfaces, repair torn tissues, or insert cushioning implants.
- Corrective Osteotomy: Surgical realignment of bones to improve weight distribution and reduce stress on affected joints.
- Joint Replacement Surgery: Recommended when conservative treatments fail. The damaged joint is replaced with a prosthetic one, often made from cobalt alloys and polyethylene to replicate natural joint surfaces. These materials are durable and biocompatible.
Consultation Recommendation
If you are experiencing joint pain, it is recommended that you consult a specialist in musculoskeletal and joint conditions at Phyathai Sriracha Hospital. Our team of experienced orthopedic surgeons specializes in joint replacement procedures for knee and hip osteoarthritis. We offer advanced treatments, including artificial joint replacement and corrective surgeries, to restore function and improve your quality of life.